Has anyone ever told you to, “Look before you leap?” If you’re thinking about leaping into a new small business, look before you leap means, create a plan.
Many businesses fail in four years and most fail in ten. There are many reasons why they fail, but the root cause is that they don’t have a good (or any) written plan.
Too often, small business owners think a plan is for getting a loan or an investor. They download a typical business plan template from the internet and fill it out. This is not the purpose of planning and isn’t what lenders are looking for. They want to see that you have thought through your business strategy and have a good implementation approach.
Also, many businesses think they build the plan once and leave it alone after that. A plan should be a living document, annually updated, and quarterly reviewed to ensure you’re on track.
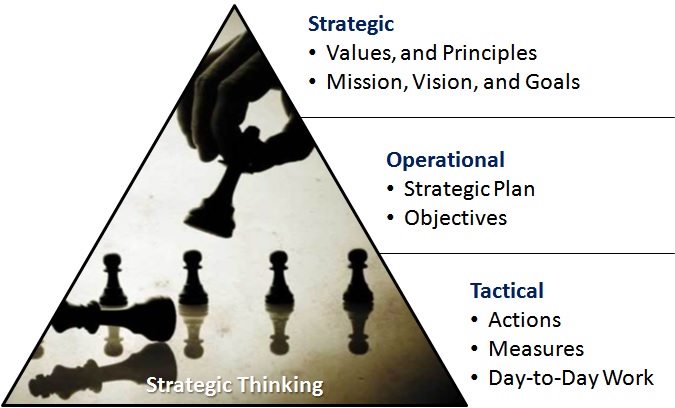
New businesses should create a “Strategic Business Plan.” This contains the typical business plan items a lender looks for, but also overcomes the five reasons 70% of all plans fail. These plans are accompanied by a current “Annual Operational Implementation Plan,” which outlines steps for the year to make the business successful.
Have you looked before you leaped?
 Many people start their own business for a variety of reasons: extra income, want to be their own boss, freedom of when and when not to work, stay at home parent, and a whole host of other reasons. However, many of these businesses fail over time, often because the owner didn’t document, follow, and constantly update a strategic business plan. The often overlooked and seldom thought about aspects of any strategic and business plan, is deep down, why you’re doing what you’re doing and where you want it to go — the mission and vision. Sure, many companies have an idea and even some of them they write it down. But, how good are these statements for your company?
Many people start their own business for a variety of reasons: extra income, want to be their own boss, freedom of when and when not to work, stay at home parent, and a whole host of other reasons. However, many of these businesses fail over time, often because the owner didn’t document, follow, and constantly update a strategic business plan. The often overlooked and seldom thought about aspects of any strategic and business plan, is deep down, why you’re doing what you’re doing and where you want it to go — the mission and vision. Sure, many companies have an idea and even some of them they write it down. But, how good are these statements for your company?



 Leadership is a dying art in the world today. The great leaders of the past are found few-and-far between these days. There are some that have been fairly successful leaders that have rose to an iconic status, but have they been truly great leaders or just really successful at running something?
Leadership is a dying art in the world today. The great leaders of the past are found few-and-far between these days. There are some that have been fairly successful leaders that have rose to an iconic status, but have they been truly great leaders or just really successful at running something?